オープンソースの統合オフィスソフト「LibreOffice」は、ドキュメントをコマンドで操作する機能を備えています。
そこでここではLibreOfficeコマンドの使用例として、ファイル形式を変換したりプリントアウトする方法を紹介します。
なお、下記にコマンドのヘルプを掲載しておりますので、すべてのコマンドラインオプションを確認したい場合にもお役立てください。
この記事は、以下の環境で実行した結果を基にしています。他のエディションやバージョンでは、動作結果が異なる場合があることをご了承ください。
| ソフトウェア | バージョン |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 Pro 64bit | 1903 |
| LibreOffice | 6.3.1.2 |
目次
コマンドの使い方
LibreOfficeをコマンドで操作する場合は、インストールフォルダー内にある「soffice.com」を利用します。64ビット版Windows 10の場合は、デフォルトで以下のフォルダー内にあります。
C:\Program Files\LibreOffice\program\
また、soffice.comコマンドを利用する際は、環境変数「PATH」にsoffice.comの場所を追加してから実行します。
環境変数への追加方法は、次のとおりです。
> set PATH=%PATH%;C:\Program Files\LibreOffice\program\;ファイル形式を変換する
最も便利な使い方は、ファイル形式の変換に利用する方法です。
たとえば、以下のコマンドでは「sample.odt」ファイルをPDF形式ファイルに変換しています。
> soffice.com --headless --convert-to pdf sample.odt変換したファイルは、デフォルトではカレントディレクトリに出力されますが、出力先を指定する場合は「--outdir」オプションで出力先を指定して、次のように実行します。
> soffice.com --headless --convert-to pdf --outdir D:\export\ sample.odtなお、変換元のファイル指定に「*(アスタリスク)」などのワイルドカードで指定して一括変換することもできるようですが、私か試した環境では利用できませんでした。
変換可能なファイルは、次のとおりです。
- Microsoft Office形式ファイル(.doc .docx .xls, .xlsx .ppt .pptx)
- テキストファイル(.txt)
- HTMLファイル(.html)
- Openドキュメント形式ファイル(.odt .odsなど)
ちなみに、コマンドで利用している「--headless」オプションは、LibreOfficeのGUIを表示せずに機能を利用する場合に指定します。
ファイルを印刷する
たとえば、以下のコマンドでは「sample.odt」ファイルを「通常使うプリンター」で印刷しています。
> soffice.com -p sample.odt「通常使うプリンター」以外で印刷する場合は、プリンター名を指定して、次のように実行します。
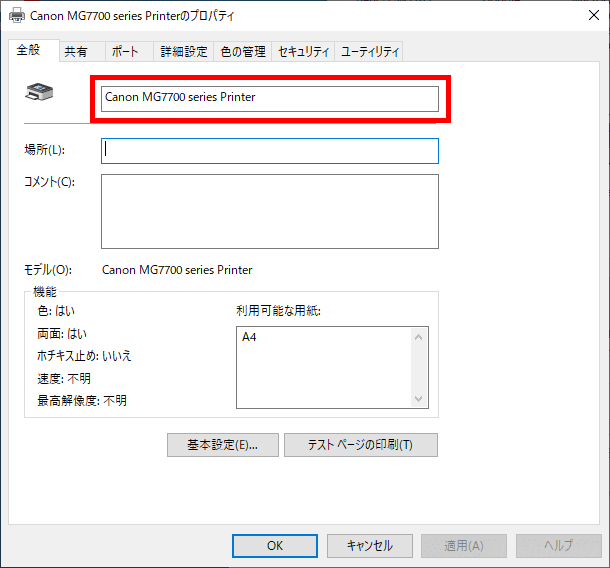
> soffice.com --pt "<プリンター名>" sample.odtなお、プリンター名はプリンターのプロパティ画面の「全般」タブで確認できます。
コマンドオプション一覧
C:\Program Files\LibreOffice\program>soffice.com --help
LibreOffice 6.3.1.2 b79626edf0065ac373bd1df5c28bd630b4424273
Usage: soffice [argument...]
argument - switches, switch parameters and document URIs (filenames).
Using without special arguments:
Opens the start center, if it is used without any arguments.
{file} Tries to open the file (files) in the components
suitable for them.
{file} {macro:///Library.Module.MacroName}
Opens the file and runs specified macros from
the file.
Getting help and information:
--help | -h | -? Shows this help and quits.
--helpwriter Opens built-in or online Help on Writer.
--helpcalc Opens built-in or online Help on Calc.
--helpdraw Opens built-in or online Help on Draw.
--helpimpress Opens built-in or online Help on Impress.
--helpbase Opens built-in or online Help on Base.
--helpbasic Opens built-in or online Help on Basic scripting
language.
--helpmath Opens built-in or online Help on Math.
--version Shows the version and quits.
--nstemporarydirectory
(MacOS X sandbox only) Returns path of the temporary
directory for the current user and exits. Overrides
all other arguments.
General arguments:
--quickstart[=no] Activates[Deactivates] the Quickstarter service.
--nolockcheck Disables check for remote instances using one
installation.
--infilter={filter} Force an input filter type if possible. For example:
--infilter="Calc Office Open XML"
--infilter="Text (encoded):UTF8,LF,,,"
--pidfile={file} Store soffice.bin pid to {file}.
--display {display} Sets the DISPLAY environment variable on UNIX-like
platforms to the value {display} (only supported by a
start script).
User/programmatic interface control:
--nologo Disables the splash screen at program start.
--minimized Starts minimized. The splash screen is not displayed.
--nodefault Starts without displaying anything except the splash
screen (do not display initial window).
--invisible Starts in invisible mode. Neither the start-up logo nor
the initial program window will be visible. Application
can be controlled, and documents and dialogs can be
controlled and opened via the API. Using the parameter,
the process can only be ended using the taskmanager
(Windows) or the kill command (UNIX-like systems). It
cannot be used in conjunction with --quickstart.
--headless Starts in "headless mode" which allows using the
application without GUI. This special mode can be used
when the application is controlled by external clients
via the API.
--norestore Disables restart and file recovery after a system crash.
--safe-mode Starts in a safe mode, i.e. starts temporarily with a
fresh user profile and helps to restore a broken
configuration.
--accept={connect-string} Specifies a UNO connect-string to create a UNO
acceptor through which other programs can connect to
access the API. Note that API access allows execution
of arbitrary commands.
The syntax of the {connect-string} is:
connection-type,params;protocol-name,params
e.g. pipe,name={some name};urp
or socket,host=localhost,port=54321;urp
--unaccept={connect-string} Closes an acceptor that was created with
--accept. Use --unaccept=all to close all acceptors.
--language={lang} Uses specified language, if language is not selected
yet for UI. The lang is a tag of the language in IETF
language tag.
Developer arguments:
--terminate_after_init
Exit after initialization complete (no documents loaded)
--eventtesting Exit after loading documents.
New document creation arguments:
The arguments create an empty document of specified kind. Only one of them may
be used in one command line. If filenames are specified after an argument,
then it tries to open those files in the specified component.
--writer Creates an empty Writer document.
--calc Creates an empty Calc document.
--draw Creates an empty Draw document.
--impress Creates an empty Impress document.
--base Creates a new database.
--global Creates an empty Writer master (global) document.
--math Creates an empty Math document (formula).
--web Creates an empty HTML document.
File open arguments:
The arguments define how following filenames are treated. New treatment begins
after the argument and ends at the next argument. The default treatment is to
open documents for editing, and create new documents from document templates.
-n Treats following files as templates for creation of new
documents.
-o Opens following files for editing, regardless whether
they are templates or not.
--pt {Printername} Prints following files to the printer {Printername},
after which those files are closed. The splash screen
does not appear. If used multiple times, only last
{Printername} is effective for all documents of all
--pt runs. Also, --printer-name argument of
--print-to-file switch interferes with {Printername}.
-p Prints following files to the default printer, after
which those files are closed. The splash screen does
not appear. If the file name contains spaces, then it
must be enclosed in quotation marks.
--view Opens following files in viewer mode (read-only).
--show Opens and starts the following presentation documents
of each immediately. Files are closed after the showing.
Files other than Impress documents are opened in
default mode , regardless of previous mode.
--convert-to OutputFileExtension[:OutputFilterName] \
[--outdir output_dir] [--convert-images-to]
Batch convert files (implies --headless). If --outdir
isn't specified, then current working directory is used
as output_dir. If --convert-images-to is given, its
parameter is taken as the target filter format for *all*
images written to the output format. If --convert-to is
used more than once, the last value of
OutputFileExtension[:OutputFilterName] is effective. If
--outdir is used more than once, only its last value is
effective. For example:
--convert-to pdf *.odt
--convert-to epub *.doc
--convert-to pdf:writer_pdf_Export --outdir /home/user *.doc
--convert-to "html:XHTML Writer File:UTF8" \
--convert-images-to "jpg" *.doc
--convert-to "txt:Text (encoded):UTF8" *.doc
--print-to-file [--printer-name printer_name] [--outdir output_dir]
Batch print files to file. If --outdir is not specified,
then current working directory is used as output_dir.
If --printer-name or --outdir used multiple times, only
last value of each is effective. Also, {Printername} of
--pt switch interferes with --printer-name.
--cat Dump text content of the following files to console
(implies --headless). Cannot be used with --convert-to.
--script-cat Dump text content of any scripts embedded in the files
to console (implies --headless). Cannot be used with
--convert-to.
-env:<VAR>[=<VALUE>] Set a bootstrap variable. For example: to set
a non-default user profile path:
-env:UserInstallation=file:///tmp/test
Ignored switches:
-psn Ignored (MacOS X only).
-Embedding Ignored (COM+ related; Windows only).
--nofirststartwizard Does nothing, accepted only for backward compatibility.
--protector {arg1} {arg2}
Used only in unit tests and should have two arguments.あとがき
コマンドで操作できると、他のコマンドと組み合わせて一括処理するなど、さまざまな処理の自動化に役立つでしょう。